The Claude Code Daily Handbook: Strategic AI Collaboration for Modern Developers

The Claude Code Daily Handbook: Strategic AI Collaboration for Modern Developers
A Strategic Guide for Professional Developers (November 2025)
Why This Claude Code Guide Exists: A Personal Note
This guide serves a dual purpose. Like many tools we use daily, Claude Code's power lies in its depth. But that depth can be easy to forget in the rush of everyday development.
I created this comprehensive reference as much for myself as for you. After months of building custom agents, skills, commands, and hooks, I realized something: the basics matter most. The advanced features are powerful, but they're built on fundamental workflows that are easy to overlook when you're moving fast.
Here's the reality: I use Claude Code every single day. It's become integral to my development process. But even as someone who's invested significant time customizing it, I find myself occasionally forgetting optimal patterns or reverting to less efficient habits.
The paradox of powerful tools: The more features they have, the easier it is to miss the core patterns that unlock their actual value.
This guide is my answer to that challenge. It's a resource I can return to when I need to recalibrate, remember why certain modes exist, or optimize my workflow. If you're reading this, you're likely in a similar position; using Claude Code regularly but wanting to squeeze more value from every session.
What you'll find here: Not just feature documentation, but the why behind each capability. The strategic thinking that transforms Claude Code from a helpful assistant into a force multiplier for your development work.
Let's dive into making every coding session with Claude more intentional and effective.
The development landscape has shifted. AI coding assistants are no longer novelties. They're production tools. But here's what most developers miss: Claude Code isn't just another autocomplete engine or chat interface. It's a true development agent that reads your codebase, writes production code, executes tests, and commits changes under your intelligent supervision.
This guide reveals the advanced workflows, configuration patterns, and integration strategies that separate casual users from masters. You'll learn to view Claude not as a passive helper, but as an agentic collaborator that amplifies your capabilities while maintaining the safety and control critical for production environments.
What you'll master:
- The three operational modes and when to use each
- Context management through hierarchical memory systems
- Plan-first workflows that mirror senior engineering practices
- Advanced integrations with MCP servers and custom sub-agents
- Production-ready safety configurations
Let's transform how you build software.
TL;DR - Key Takeaways
For busy developers: Here are the 5 pillars that separate casual Claude Code users from masters:
- Three Operational Modes - Normal (safety), Plan (strategy), Auto-Accept (speed). Know when to use each.
- CLAUDE.md Memory System - Create persistent context that cascades from enterprise to global user memory to project level.
- Plan-First Workflows - Think strategically before implementing, like senior engineers.
- MCP Integration - Connect Claude to your entire ecosystem (GitHub, databases, APIs, custom tools).
- Production Safety - Granular permissions, checkpoints, and workflow automation for enterprise use.
Part 1: Foundation - Understanding Your AI Agent
The Paradigm Shift: What Makes Claude Code Different
Stop thinking of Claude Code as a smart autocomplete tool. That mental model limits you.
Claude Code operates as a true agent within your development environment. Here's what that means in practice:
Claude Code can:
- Read entire codebases, documentation, and dependency graphs
- Write and edit multiple files with surgical precision
- Execute bash commands, run tests, and verify builds
- Commit changes to version control (with your approval)
- Integrate with external tools via MCP servers
- Delegate specialized tasks to custom sub-agents
This isn't autocomplete that suggests the next line. This is an active development partner that understands context, plans strategically, and executes complex multi-file refactorings.
The critical difference: Traditional AI coding tools work at the line or function level. Claude Code works at the project level, understanding architecture, dependencies, and the broader context of your changes.
The Three Operational Modes: Choose Your Speed
Claude Code features three distinct operational modes, each optimized for specific development phases. Master when to use each, and you'll unlock productivity gains that feel like having an extra senior engineer on your team.
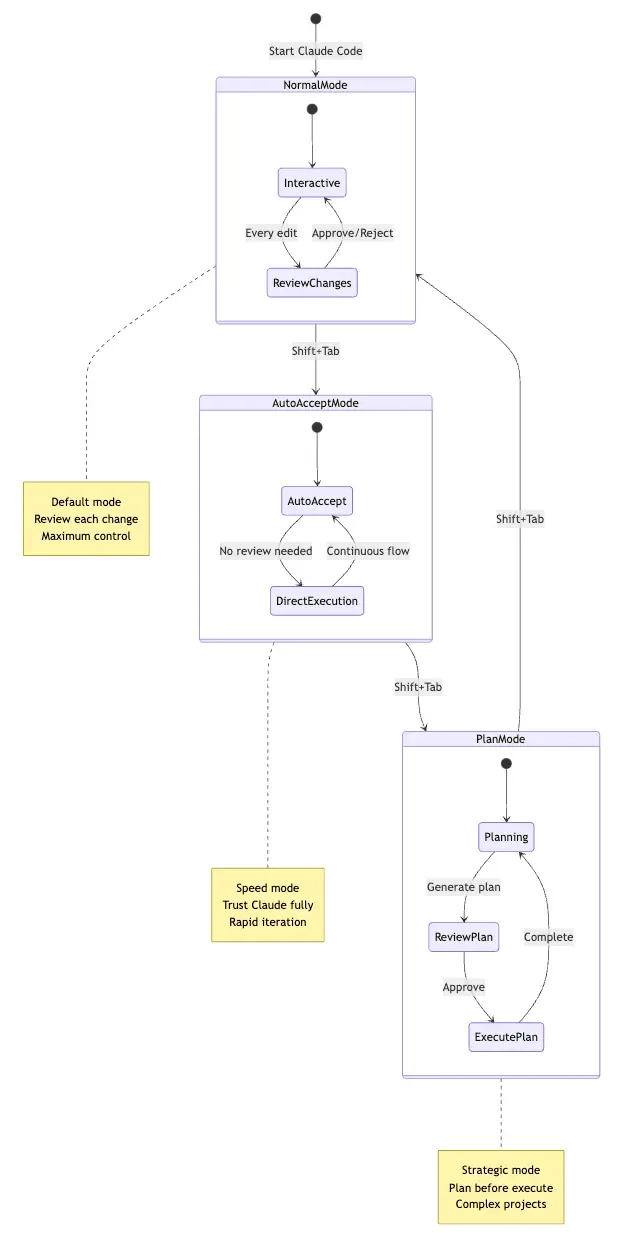
Switch between modes: Press Shift+Tab to cycle through Normal → Auto-Accept → Plan → Normal.
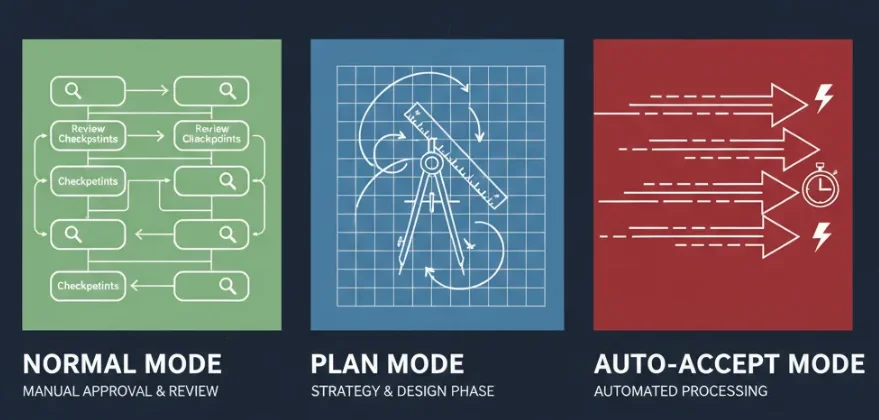
Normal Mode: Maximum Control (Default)
When you're coding: Normal Mode serves as your safety net.
Every file edit, every bash command; Claude pauses and asks for approval. This might seem slow at first, but it's invaluable when:
- Exploring unfamiliar codebases where you need to verify each step
- Making high-stakes changes to production systems
- Learning new patterns and wanting visibility into Claude's reasoning
- Debugging complex issues where you need to understand each transformation
Real-world example: You're investigating a performance bottleneck in a microservices architecture you didn't build. Normal Mode lets you approve each file Claude reads and each profiling command it runs, ensuring you understand the system as you debug.
Pro tip: Normal Mode is perfect for pairing with junior developers. They see every decision Claude makes, turning each session into a learning opportunity.
Plan Mode: Think Before You Act
Activate: Press Shift+Tab twice
This mode transforms Claude into a read-only research and planning agent. It cannot execute changes, only analyze, research, and formulate strategies.
Think of Plan Mode as your virtual architect. It:
- Reads your codebase and documentation thoroughly
- Analyzes dependencies and potential side effects
- Formulates detailed implementation strategies
- Generates design documents and specifications
- Identifies edge cases and testing requirements
This mirrors senior engineering best practices: Understand the system first, design a solution second, implement third. It prevents the costly "ready, fire, aim" pattern that leads to technical debt.
Real-world example: You need to migrate a monolithic Express app to a microservices architecture. Activate Plan Mode and ask Claude to:
- Analyze the current codebase structure
- Identify service boundaries
- Design the migration strategy
- Create a phased implementation plan
- Document risks and rollback procedures
Claude spends 5-10 minutes reading code, then delivers a comprehensive plan. You review, iterate, and approve. Only then do you exit Plan Mode and execute.
The payoff: You avoid architectural mistakes that would take days to unwind.
Auto-Accept Mode: Rapid Iteration
Activate: Press Shift+Tab once
This mode automatically applies file edits without interrupting you for approval. It's your speed boost for straightforward tasks where you trust the direction.
Critical safety note: Auto-Accept Mode still respects your permission rules. Operations marked as "deny" remain blocked. Commands in the "ask" category still trigger prompts. You're accelerating safe operations, not bypassing safety.
When to use Auto-Accept:
- Clear refactoring tasks: "Convert all class components to functional components"
- Batch updates: "Update all API calls to use the new v2 endpoint"
- Code style fixes: "Apply consistent formatting across the frontend"
- Routine migrations: "Upgrade all React imports to React 18 syntax"
When NOT to use Auto-Accept:
- Unfamiliar codebases where surprises lurk
- High-risk production changes
- Complex logic transformations
- Database migrations or API contract changes
Real-world example: You have 50 React class components that need conversion to hooks. You verify the first two conversions in Normal Mode to ensure Claude understands the pattern. Then you switch to Auto-Accept and watch it transform the remaining 48 files in minutes.
Pro tip: Set a checkpoint (type checkpoint) before entering Auto-Accept Mode. If anything goes wrong, you can /rewind to the checkpoint instantly.
The Thinking Spectrum: Allocating Cognitive Resources
Not all problems are created equal. A simple variable rename needs minimal reasoning. A complex architectural decision deserves deep analysis. Claude Code lets you allocate computational resources dynamically based on trigger words in your prompts.
This is like having a "think harder" button with three levels.
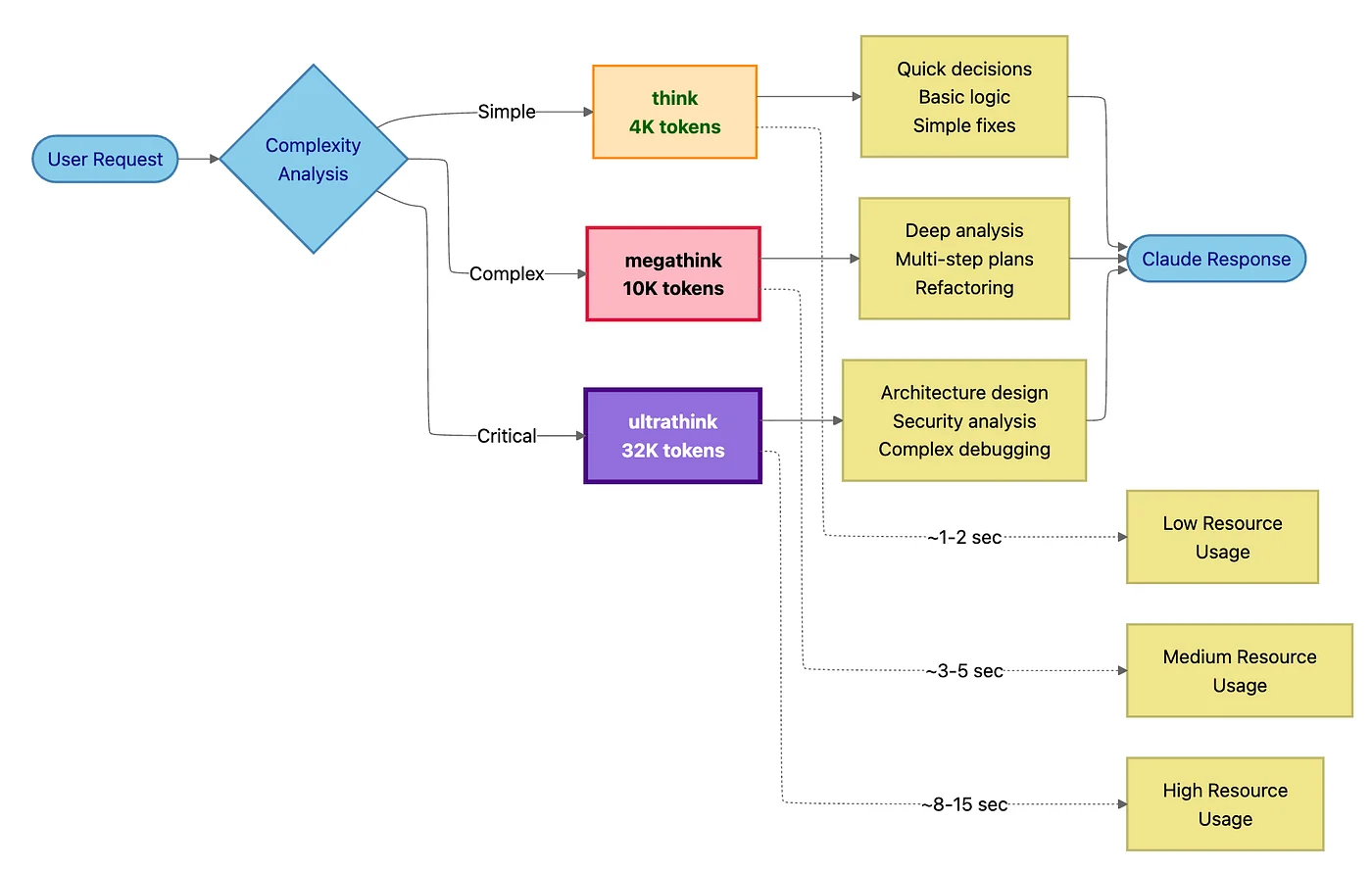
The Three Thinking Levels
When to Use Each Level:
Standard (no trigger): Your default for everyday coding.
- Simple refactoring
- Adding features to familiar code
- Writing tests for straightforward logic
- Documentation updates
"think" (4K tokens): When edge cases matter.
- Implementing error handling with multiple failure modes
- Designing database queries with performance implications
- Handling user input validation with security considerations
- Refactoring functions with subtle dependencies
"megathink" (10K tokens): For architectural thinking.
- Planning multi-file refactorings
- Designing new feature architectures
- Optimizing performance bottlenecks
- Migrating between major library versions
"ultrathink" (32K tokens): For mission-critical decisions.
- Security audits and threat modeling
- Investigating mysterious production bugs in unfamiliar codebases
- Designing system architectures from scratch
- Analyzing complex legacy code before refactoring
Real-World Example: API Rate Limiting
Without thinking:
"Add rate limiting to our API"
Claude implements basic rate limiting, might miss distributed system edge cases.
With megathink:
"megathink Design and implement rate limiting for our API. Consider:
- Distributed systems (multiple server instances)
- Different limits for authenticated vs. anonymous users
- Graceful degradation under attack
- Monitoring and alerting"
Claude analyzes distributed race conditions, designs Redis-backed rate limiting with sliding windows, implements proper error responses, and adds metrics.
The difference: 10 extra seconds of thinking prevents days of debugging in production.
Making Thinking Persistent
Press Tab: Toggle persistent thinking mode. Every response uses enhanced reasoning until you toggle it off.
When to enable persistent thinking:
- Working in an unfamiliar codebase
- Debugging a complex issue requiring multiple rounds
- Planning a major feature implementation
- Pair programming with Claude on architectural decisions
When to disable:
- Simple, repetitive tasks
- Following an established pattern
- Making routine updates
Pro tip: Thinking modes consume more tokens, which may affect API costs. Use them intentionally - like a senior engineer's time, they're valuable but not free.
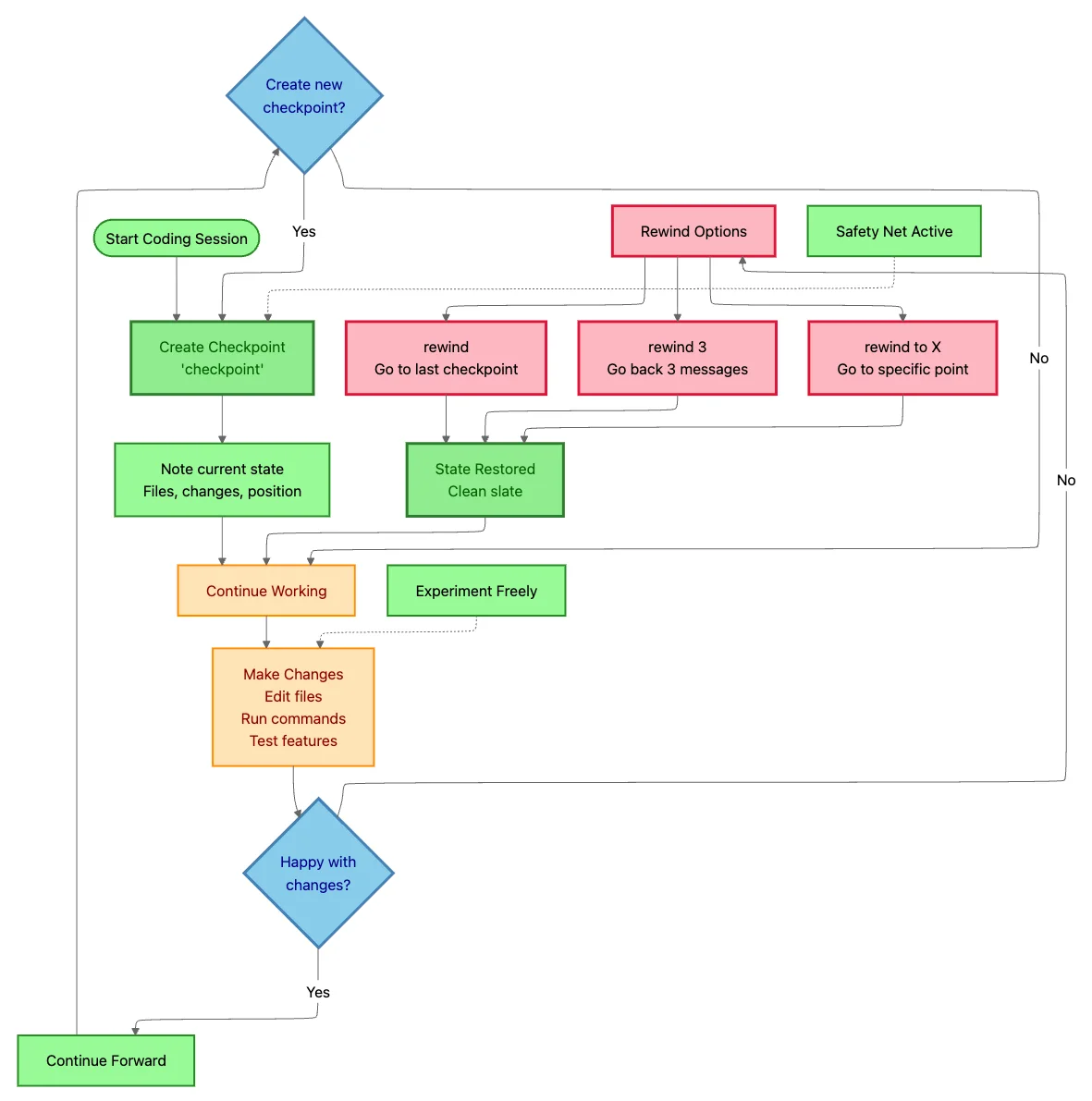
The Safety Net: Checkpoints and Rewind
Here's a liberating truth: You can't break anything permanently with Claude Code.
The checkpoint system, introduced in v2.0, creates automatic snapshots before Claude makes changes. Think of it as Git for your conversation with Claude, except it tracks both code AND context.
The Video Game Analogy: Claude Code Checkpoints = Save Points
If you grew up in the 80s and 90s, you already understand checkpoints intuitively. Remember fighting your way through Prince of Persia, finally reaching that difficult level, and hitting save? You'd battle the final boss over and over, dying repeatedly, but always respawning at your save point. No lost progress. Just pure learning and iteration.
Claude Code checkpoints work exactly like those classic game save points.
Except instead of fighting the Jaffar, you're wrestling with:
- Complex refactoring challenges
- Tricky bug fixes that require multiple attempts
- Architectural decisions with uncertain outcomes
- Migration tasks that might break everything
The gameplay loop:
- Save your progress: Create a checkpoint before attempting something risky
- Try the boss fight: Let Claude make bold changes
- Did you win? Great! Create another checkpoint and move forward
- Did you die? No problem! Rewind to your last save and try a different strategy
- Repeat until victory: Each attempt teaches you more about the problem
Why this changes everything:
In classic games, that save system meant you could experiment fearlessly. Try crazy strategies. Take risks. Learn from failure without consequence. The same psychology applies to development with Claude Code.
Without checkpoints: You code conservatively, making tiny incremental changes, terrified of breaking something.
With checkpoints: You code boldly, trying ambitious refactorings, knowing you can always respawn at your last save.
The result: Faster development, better solutions, and way more fun. Just like those classic games, except now you're leveling up your codebase instead of your character.
Achievement Unlocked: Fearless Developer
Creating Checkpoints: Your Coding Save Points
Manual checkpoint creation:
checkpoint
Claude saves the current state: all file contents, conversation history, and context. Name it for clarity:
checkpoint before-migration
When to create checkpoints:
- Before starting a major refactoring
- After completing a working feature (before adding the next)
- When entering Auto-Accept Mode for batch changes
- Before experimenting with an unfamiliar approach
Think of checkpoints like:
- Git commits (but local and instant)
- Video game save points (try risky moves without consequence)
- Science experiments (test hypotheses safely)
Rewinding: Time Travel for Coding
Made a mistake? Claude went down the wrong path? No problem.
Access the rewind menu:
- Press Esc+Esc, or
- Type
/rewind
Three rewind modes:
Conversation only → Undo Claude's messages but keep code changes
- Use when: The code is fine, but the conversation went off-track
Code only → Revert file changes but keep the conversation
- Use when: Claude edited the wrong files, but the discussion is valuable
Both → Complete reset to the checkpoint
- Use when: Everything needs to start over
Granular rewind options:
rewind # Go to last checkpoint
rewind 3 # Go back 3 messages
rewind to X # Go to specific checkpoint "X"
Real-World Example: Fearless Refactoring
You're converting a JavaScript codebase to TypeScript, a notoriously risky migration.
Traditional approach: Careful, incremental changes with constant manual testing. Fear of breaking everything. Days of work.
With checkpoints:
- Create checkpoint:
checkpoint pre-typescript - Ask Claude: "Convert the entire codebase to TypeScript"
- Claude converts 50 files in Auto-Accept Mode
- Run tests → 12 tests fail
- Investigate failures → Claude misunderstood an implicit type contract
- Type:
/rewind→ Select "Code only" - Refine prompt: "Convert to TypeScript. The
UserDataobject must allow optionalemailfield." - Claude reconverts with correct types
- Tests pass
Time saved: Hours. Stress level: Zero. Code quality: Higher (because you experimented boldly).
Critical Limitation: Bash Commands
Important: Checkpoints track file edits made by Claude, but not changes from bash commands.
If Claude runs npm install and modifies package-lock.json, that change happens outside the checkpoint system. Use Git for those changes or be cautious with destructive bash commands.
Best practice: Configure your .claude/settings.json to require approval for risky commands:
{
"permissions": {
"ask": [
"Bash(rm:*)",
"Bash(npm install:*)",
"Bash(git reset:*)"
]
}
}
Part 2: Mastery - Claude Code Context Management and Strategic Workflows
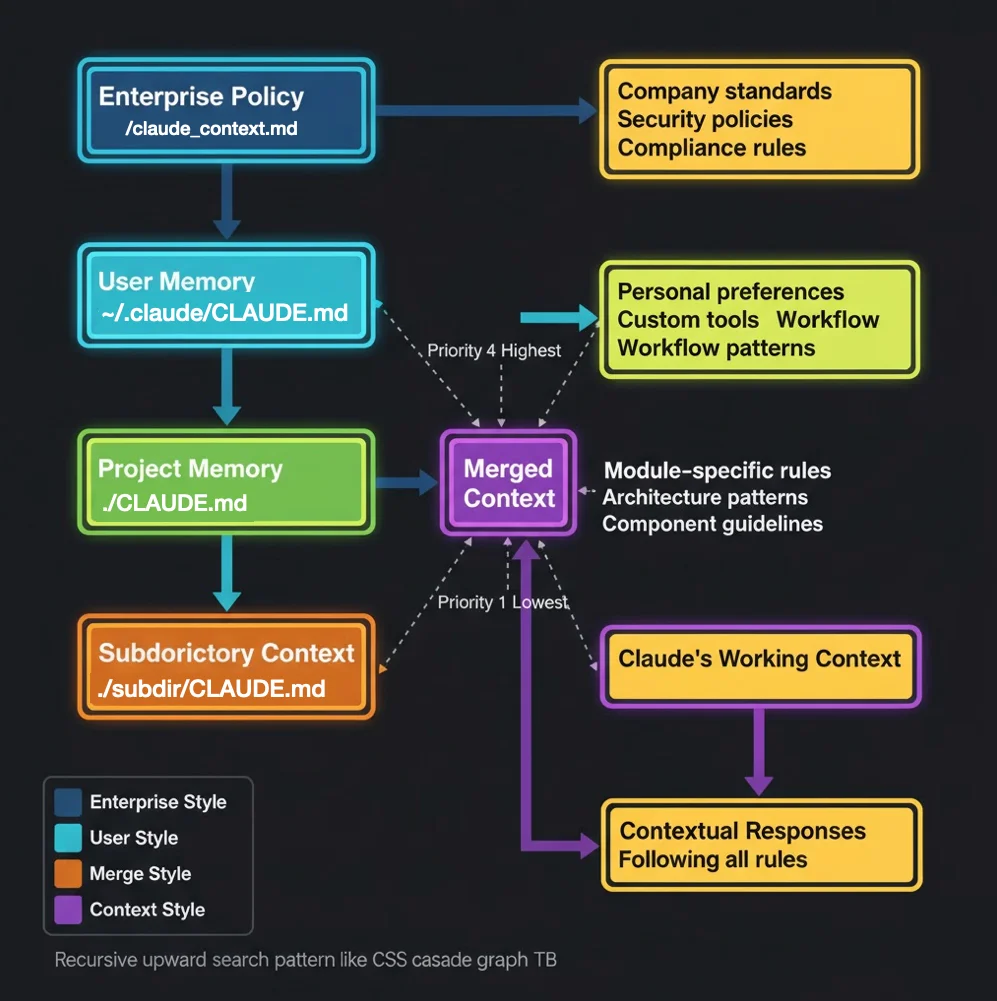
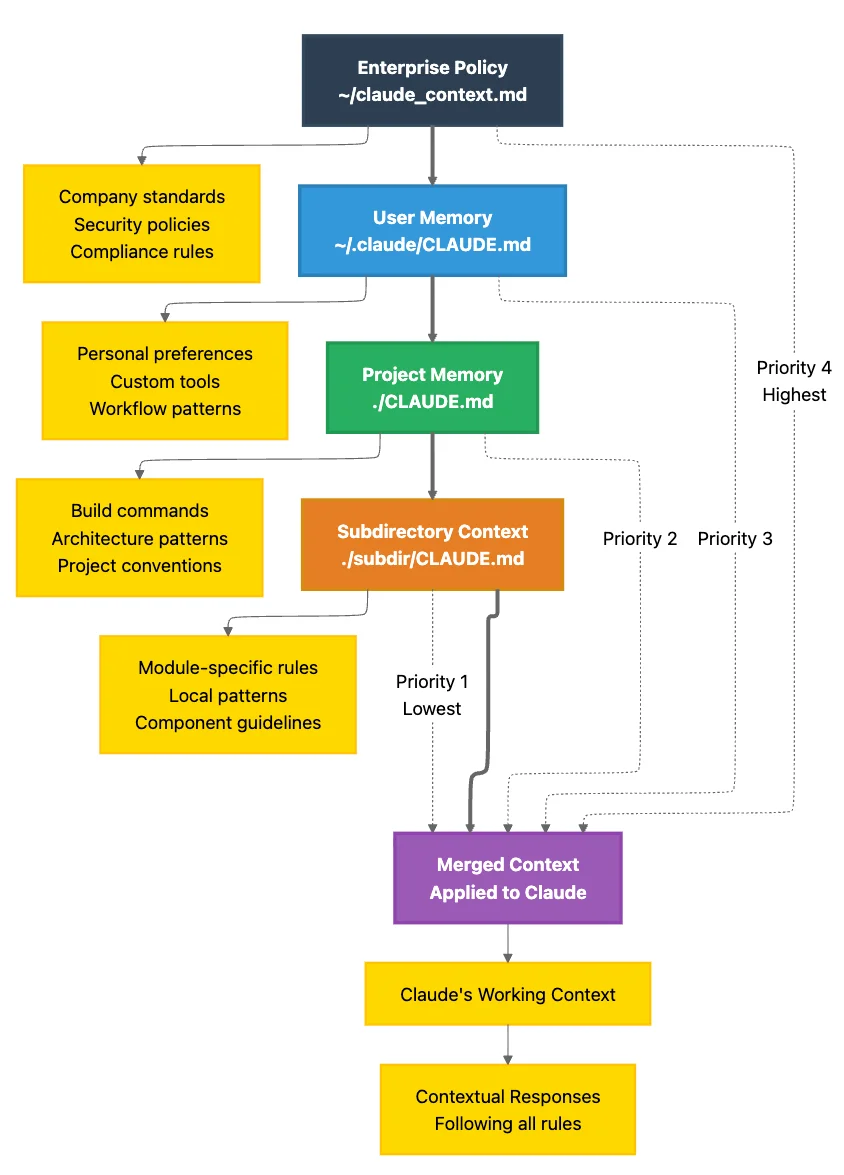
The CLAUDE.md Hierarchical Memory System
Here's the secret to making Claude Code feel like a team member who's been on your project for months: persistent context.
Most developers use Claude Code like a stateless chatbot, re-explaining project structure, conventions, and build commands in every session. Masters use the CLAUDE.md hierarchical memory system to create a knowledge base that cascades from enterprise policies to module-specific patterns.
The result: Claude remembers everything. Your coding standards. Your build process. Your testing strategy. Your team's conventions. Every single session.
The Four-Level Context Cascade
Claude loads CLAUDE.md files by searching recursively upward from your current directory. More specific instructions override or extend general ones, like CSS cascade rules but for AI memory.
Level 1: Enterprise Policy (Highest Priority)
- Path:
/Library/Application Support/ClaudeCode/CLAUDE.md(macOS system-wide) - Managed by: IT, DevOps, Security teams
- Scope: Every project, every developer, company-wide
- Use for:
- Security policies ("Never commit API keys")
- Compliance requirements (HIPAA, SOC2, GDPR)
- Mandatory coding standards
- Prohibited operations
Level 2: User-Level Memory
- Path:
~/.claude/CLAUDE.md - Managed by: Individual developer
- Scope: All your personal projects
- Use for:
- Personal preferences
- Global tool configurations
- Common patterns you use across projects
Level 3: Project-Level Memory
- Path:
./CLAUDE.mdin project root - Managed by: Project lead or team
- Scope: Entire project
- Use for:
- Project architecture and conventions
- Build and test commands
- Technology stack specifics
- Team coding standards
Level 4: Module-Level Memory
- Path:
./module/CLAUDE.mdin subdirectories - Managed by: Module owners
- Scope: Specific modules or features
- Use for:
- Module-specific patterns
- API contracts for that module
- Testing requirements unique to the module
Plan-First Workflows: The Strategic Development Pattern
Here's how senior engineers approach complex features - and how you can teach Claude to do the same.
The Plan-First Workflow
Step 1: Activate Plan Mode
Press Shift+Tab twice to enter Plan Mode.
Step 2: Define the Challenge
"megathink I need to implement user authentication with OAuth for Google and GitHub.
Review:
@src/
@package.json
@docs/current-architecture.md
Goals:
- Secure JWT-based session management
- Support Google and GitHub OAuth
- Integrate with existing user database
Constraints:
- Must maintain backward compatibility
- Minimize changes to existing API routes"
Step 3: Allow Claude Code Time for Research
Claude will spend 5-10 minutes (for complex tasks) reading your codebase:
- Analyzing file structure and dependencies
- Understanding existing patterns
- Identifying integration points
- Researching potential approaches
Don't interrupt this phase. This deep analysis prevents the "start coding, hit unexpected issues, refactor painfully" cycle.
Step 4: Review the Generated Plan
Claude produces a strategic implementation plan, typically including:
- Analysis summary: Current state and constraints
- Proposed architecture: How components will interact
- File changes: What needs modification or creation
- Testing strategy: Unit, integration, and E2E tests
- Deployment considerations: Rollout steps and rollback procedures
- Risks and alternatives: Trade-offs of the chosen approach
Step 5: Iterate on the Plan
The first plan is rarely perfect. Request modifications:
This looks good, but:
- Don't implement GitHub OAuth yet, just Google for MVP
- Add password reset functionality
- Use httpOnly cookies instead of localStorage for tokens (XSS protection)
- Include rate limiting implementation details
Claude regenerates the plan with your feedback. Repeat until you're satisfied.
Step 6: Exit Plan Mode
Once the plan is approved, press Shift+Tab twice again to exit Plan Mode.
Step 7: Execute the Plan
Now Claude can implement:
"Implement the authentication plan we just created. Follow it step by step."
Claude executes methodically, referring back to the approved plan. You get:
- Consistent implementation
- No architectural surprises
- Clear progress tracking
- Easy rollback (you have the plan as documentation)
Part 3: Advanced Integration - Using Claude Code with MCP, Sub-Agents, and Production Patterns
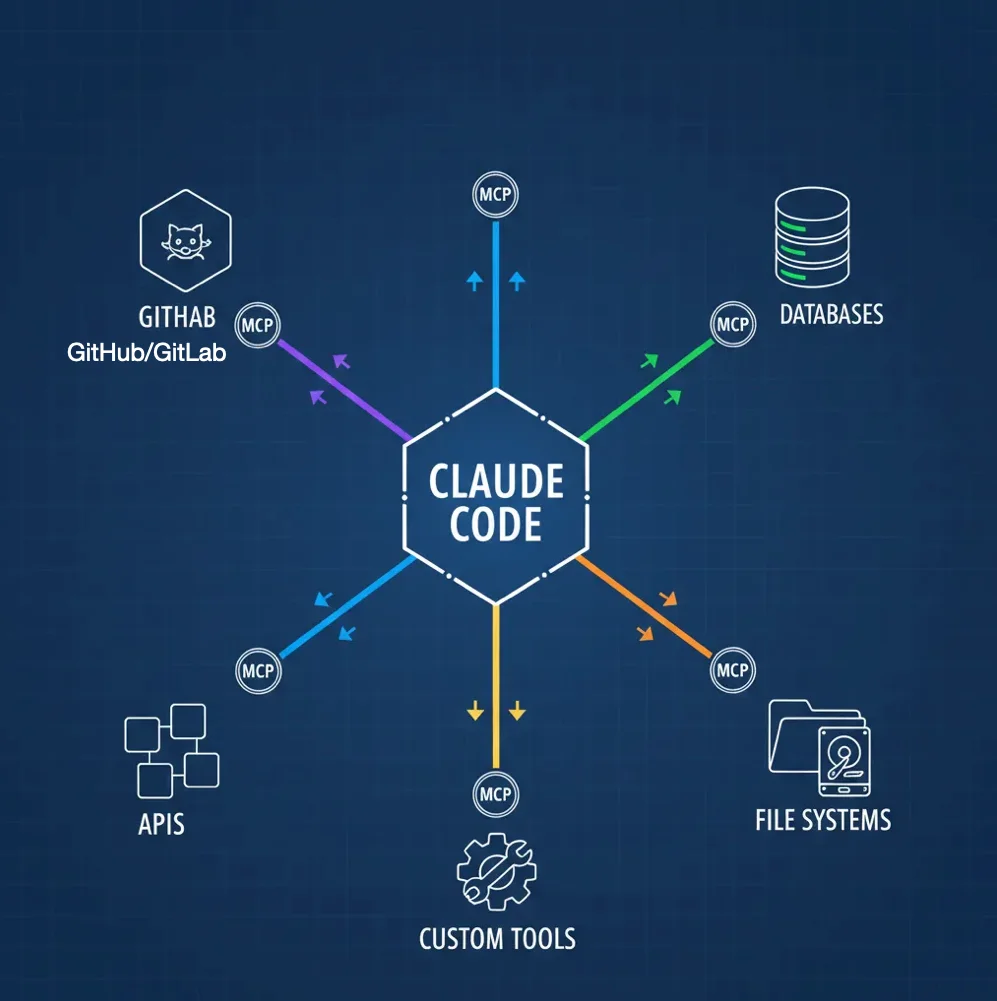
Model Context Protocol (MCP): Connecting Claude to Your Ecosystem
Claude Code is powerful in isolation. But the real magic happens when you connect it to your development ecosystem: cloud providers, project management tools, databases, error tracking services, internal APIs.
MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers act as bridges, giving Claude direct access to external tools and data sources. Think of MCP as a plugin system that transforms Claude from a code assistant into an orchestrator of your entire development workflow.
Learn more about MCP and explore available servers at the official Model Context Protocol repository and browse community servers at mcp.run.
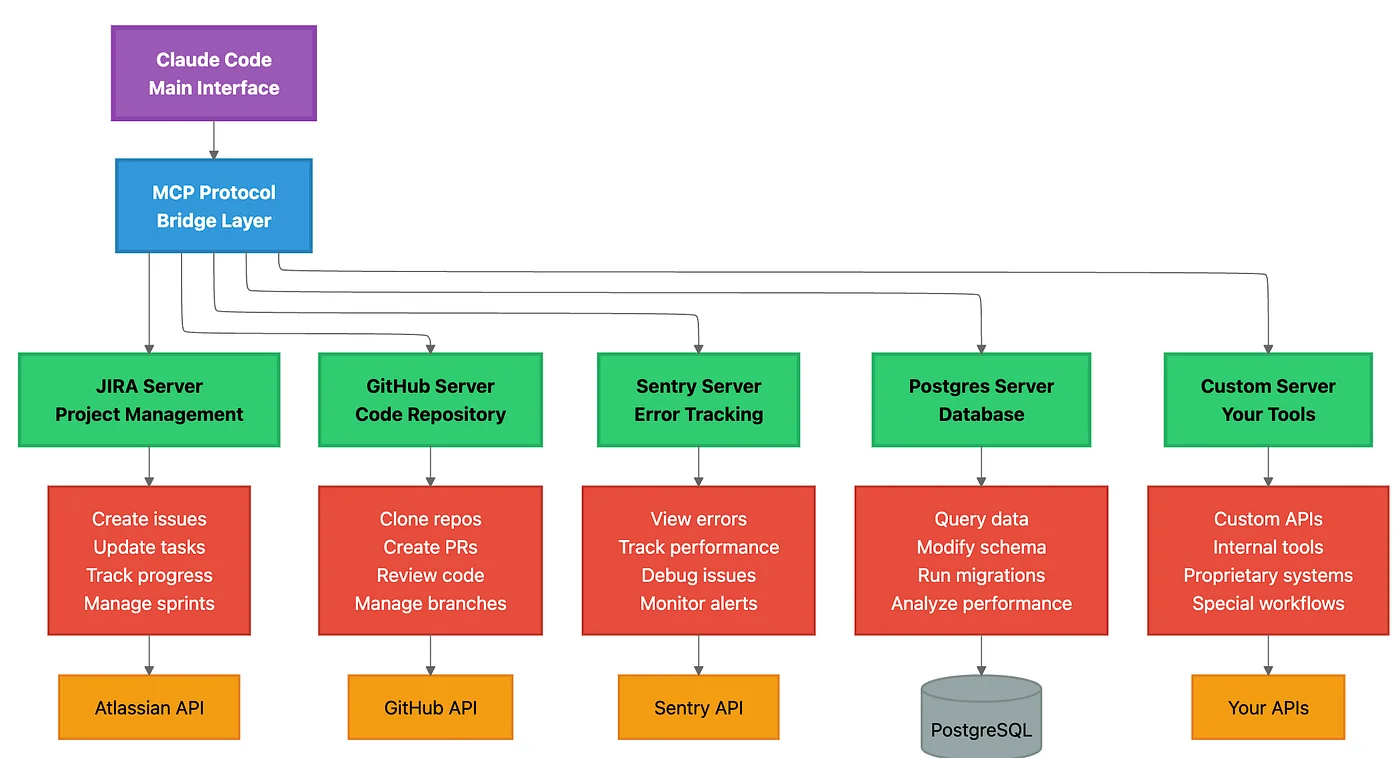
What MCP Servers Enable
Real-world example workflow (without MCP):
- You: "Fix the top priority bug"
- Switch to Linear → Find bug PROJ-123 → Read description
- Switch to Sentry → Search for related errors → Copy stack trace
- Switch to Claude Code → Paste bug details → Ask for fix
- Claude fixes bug
- Switch to GitHub → Create PR manually
- Switch to Linear → Update issue status manually
With MCP servers configured:
- You: "Fix the top priority bug from our Linear board"
- Claude automatically:
- Connects to Linear via MCP → Fetches PROJ-123 (top priority)
- Connects to Sentry via MCP → Retrieves crash logs and stack trace
- Analyzes the error in your codebase
- Proposes and implements the fix
- Creates GitHub PR via MCP
- Updates Linear issue status via MCP → "In Review"
- Posts PR link in Linear comments
You saved: 5 context switches, 10 minutes, and mental load.
Three Scopes for MCP Configuration
1. Local Scope (./.mcp.json in project root)
- Visibility: Only this project, only you
- Use for: Project-specific integrations (project database, project-specific APIs)
- Not committed to version control (add to
.gitignore)
2. User Scope (~/.config/claude-code/mcp_settings.json)
- Visibility: All your projects
- Use for: Personal tools (your GitHub account, your Linear workspace, your database credentials)
3. Project-Shared Scope (./.mcp.json committed to repo)
- Visibility: All team members
- Use for: Team-shared integrations (team Linear workspace, shared staging database, company GitHub org)
- Committed to version control
Popular MCP Integrations
GitHub MCP Server
{
"mcpServers": {
"github": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-github"],
"env": {
"GITHUB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN": "ghp_your_token_here"
}
}
}
}
Capabilities:
- Create and manage pull requests
- Review code and add comments
- Manage issues and projects
- Clone repositories
- Search code across repos
Linear MCP Server
{
"mcpServers": {
"linear": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-linear"],
"env": {
"LINEAR_API_KEY": "lin_api_your_key_here"
}
}
}
}
Perplexity MCP Server (Web research)
{
"mcpServers": {
"perplexity": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-perplexity"],
"env": {
"PERPLEXITY_API_KEY": "pplx_your_key_here"
}
}
}
}
IDE Integration: Seamless Development
Visual Studio Code: Native Extension (Recommended)
Install the official Claude Code extension from the VS Code Marketplace for the smoothest experience.
Why it's the best experience:
Released September 2025, the native VS Code extension makes Claude Code feel like a built-in IDE feature.
Key features:
- Quick Launch: Press Cmd/Ctrl+Esc → Claude opens with current file context
- Automatic Error Context:
- VS Code's Problems panel errors automatically shared with Claude
- Claude sees TypeScript errors, ESLint warnings, test failures
- No need to copy-paste error messages
- Inline Diff Review:
- Claude's changes appear as Git-style diffs in your editor
- Accept/reject changes with a single click
- See before/after side-by-side
- Dedicated Sidebar:
- Full conversation history
- Quick access to commands
- Checkpoint/rewind controls
- Mode switching (Normal/Auto-Accept/Plan)
- Smart Context Sharing:
- Current file automatically included
- Selected text sent as context
- Workspace files easily referenced with autocomplete
JetBrains IDEs: Plugin-Based
Beta plugin available for: IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, WebStorm, Rider, GoLand, and all other JetBrains IDEs.
Remote Development Note:
If using Remote Development or WSL:
- Install the plugin on the remote host, not just the local client
- Configure API keys on the remote machine
- CLAUDE.md files should be in the remote filesystem
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue 1: Subdirectory CLAUDE.md Not Loading
Problem: Claude doesn't follow patterns in ./services/payment/CLAUDE.md
Solution: Explicitly reference a file in the subdirectory:
"Refactor the payment service. Start by reviewing @./services/payment/src/stripe.ts"
Issue 2: Tab Key Not Completing Files
Problem: Pressing Tab toggles thinking mode instead of completing file paths.
Solution: File completion only works within @ references:
You: "Review @src/ [Press Tab here]
→ Autocompletes to @src/api/, @src/components/, etc.
Issue 3: Auto-Accept Mode Not Working
Problem: Claude still asks for approval on file edits in Auto-Accept Mode.
Solution: Move Edit to allow list in .claude/settings.json:
{
"permissions": {
"allow": ["Edit", "Read", "MultiEdit"],
"ask": ["Write", "Bash(git commit:*)"]
}
}
Issue 4: MCP Server Not Connecting
Diagnosis steps:
- Check MCP config location:
cat ~/.config/claude-code/mcp_settings.json - Verify server command manually
- Check Claude logs:
/doctor
Quick Reference Tables
Keyboard Shortcuts
- Shift+Tab (2x) - Toggle Plan Mode: Enter/exit read-only planning mode
- Shift+Tab (cycle) - Cycle modes: Normal → Auto-Accept → Plan
- Tab - Toggle thinking: Enable persistent enhanced reasoning
- Esc+Esc - Rewind menu: Undo code or conversation changes
- Ctrl+C - Cancel: Stop current generation
- Ctrl+D - Exit: End Claude session
- Ctrl+L - Clear screen: Visual refresh
- Ctrl+O - Verbose output: Show tool execution details
- Ctrl+R - History search: Recall previous prompts
- Ctrl+G - External editor: Open $EDITOR for multiline input
- \ + Enter - Multiline input: Continue prompt on new line
- Cmd/Ctrl+Esc - Quick launch: Open Claude with context in VS Code
Essential Slash Commands
/help- Show all commands/config- Configure settings/model- Switch AI models (e.g.,/model haiku-4.5for faster responses)/clear- Clear conversation/rewind- Undo changes/resume- Resume previous session/export- Export conversation as Markdown/mcp- Manage MCP servers/agents- Manage sub-agents/hooks- Configure workflow hooks/plugin- Manage plugins/permissions- Configure tool access/memory- Edit CLAUDE.md/context- Debug context issues/doctor- Validate configuration
Thinking Modes Quick Reference
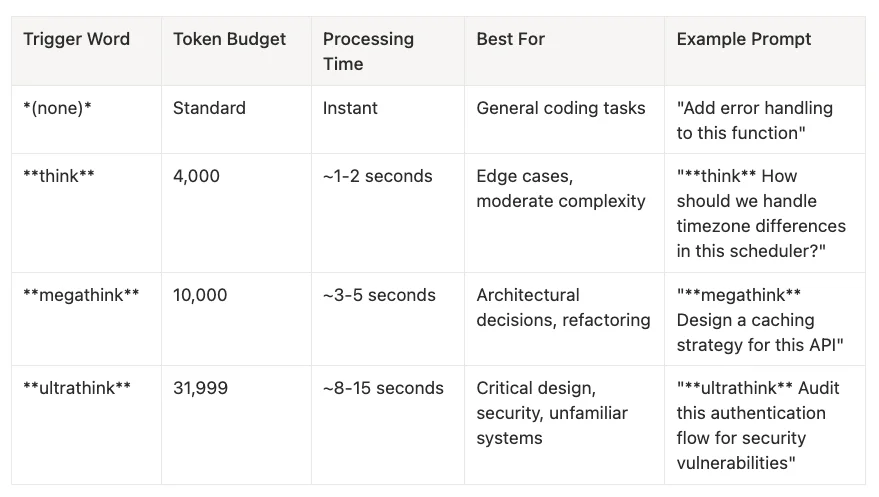
Standard (default): Normal tokens, instant response. Best for routine coding.
Think: Trigger with think in prompt. Uses 4,000 tokens, ~1-2s. Best for edge cases.
Megathink: Trigger with megathink in prompt. Uses 10,000 tokens, ~3-5s. Best for architecture.
Ultrathink: Trigger with ultrathink in prompt. Uses 31,999 tokens, ~8-15s. Best for security audits.
Persistent: Press Tab to toggle. Best for multi-turn discussions.
Conclusion: Embracing Agentic Collaboration
You've reached the end of this guide, but the beginning of a new way of building software.
What you've learned:
- Operational mastery: Three modes (Normal, Plan, Auto-Accept) for different development phases
- Context management: CLAUDE.md hierarchical memory for persistent, project-specific knowledge
- Strategic workflows: Plan-first development, fearless refactoring with checkpoints
- Advanced integrations: MCP servers connecting Claude to your ecosystem
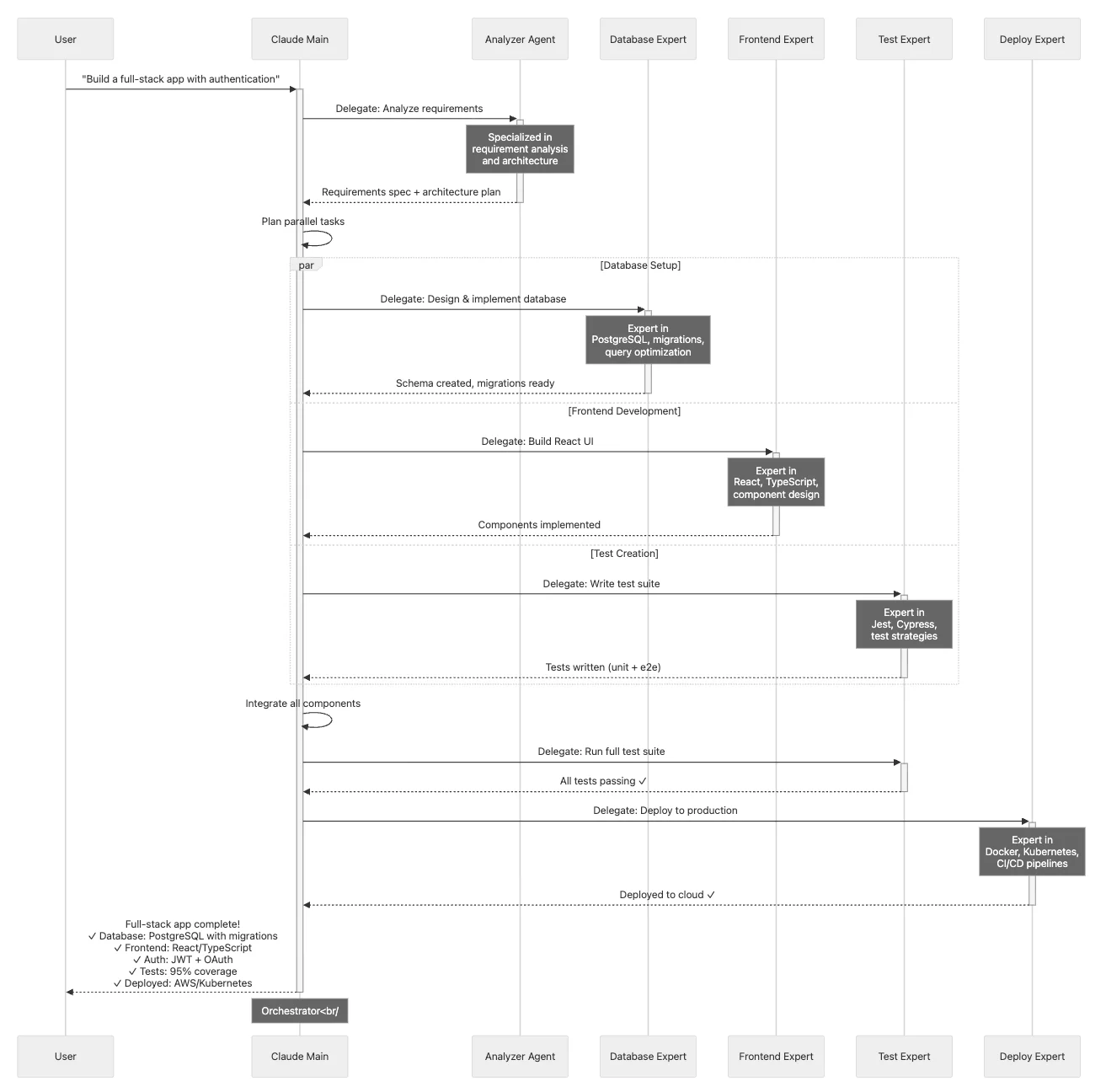
- Multi-agent orchestration: Specialized sub-agents for parallel, expert-level work
- Production safety: Granular permissions and workflow automation
The paradigm shift:
Traditional development: You write code. You run tests. You debug. You deploy.
Agentic collaboration: You define outcomes. Claude orchestrates execution. You approve results.
You're still in control. But you've amplified your capabilities:
- What took hours now takes minutes
- What required deep expertise across multiple domains now taps specialized sub-agents
- What created anxiety (risky refactoring, complex migrations) now feels safe with checkpoints
- What consumed mental energy (context switching between tools) now flows through MCP
The five pillars of mastery:
- Plan Mode for architecture - Think strategically before implementing
- CLAUDE.md for memory - Build persistent knowledge that compounds
- Permissions for safety - Define boundaries that protect production
- MCP for integration - Connect Claude to your entire development workflow
- Sub-agents for expertise - Delegate specialized tasks to focused AI experts
As Claude Code evolves (and it's evolving rapidly), these strategic principles remain constant. You're not learning a tool. You're learning a development philosophy: human and AI as collaborative partners, each contributing their unique strengths.
The future isn't human-only development. It isn't AI-only development. It's human + AI, working as a unified team.
Claude Code is your entry point to that future.
Now go build something remarkable.
About the Author
I am Rick Hightower, a seasoned professional with experience as an executive and data engineer at a Fortune 100 financial technology organization. My work there involved developing advanced Machine Learning and AI solutions designed to enhance customer experience metrics. I maintain a balanced interest in both theoretical AI concepts and their practical applications in enterprise environments.
My professional credentials include TensorFlow certification and completion of Stanford's Machine Learning Specialization program, both of which have significantly contributed to my expertise in this field. I value the integration of academic knowledge with practical implementation.
Connect with Richard on LinkedIn or Medium for additional insights on enterprise AI implementation.
Community Extensions & Resources
The Claude Code community has developed powerful extensions that enhance its capabilities. Here are some valuable resources from Spillwave Solutions:
Integration Skills
- Notion Uploader/Downloader: Seamlessly upload and download Markdown content and images to Notion
- Confluence Skill: Upload and download Markdown content and images to Confluence
- JIRA Integration: Create and read JIRA tickets, including handling special required fields
Advanced Development Agents
- Architect Agent: Puts Claude Code into Architect Mode to manage multiple projects
- Project Memory: Store key decisions, recurring bugs, tickets, and critical facts
- Claude Agents Collection: A comprehensive collection of 15 specialized agents
Visualization & Design Tools
- Design Doc Mermaid: Specialized skill for creating professional Mermaid diagrams
- PlantUML Skill: Generate PlantUML diagrams from source code
- Image Generation: Uses Gemini Banana to generate images
AI Model Integration
- Gemini Skill: Delegate specific tasks to Google's Gemini AI
Explore more at Spillwave Solutions - specialists in bespoke software development and AI-powered automation.
Tags: #ClaudeCode #AnthropicClaudeCode #AgenticAI #SoftwareEngineering #SoftwareDevelopment
Discover AI Agent Skills
Browse our marketplace of 41,000+ Claude Code skills, agents, and tools. Find the perfect skill for your workflow or submit your own.
